Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments

Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness that primarily affects young children. While it may sound alarming, HFMD is typically mild and resolves on its own within a week. In this article, we will discuss what HFMD is, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options to help you manage this condition effectively.
What is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
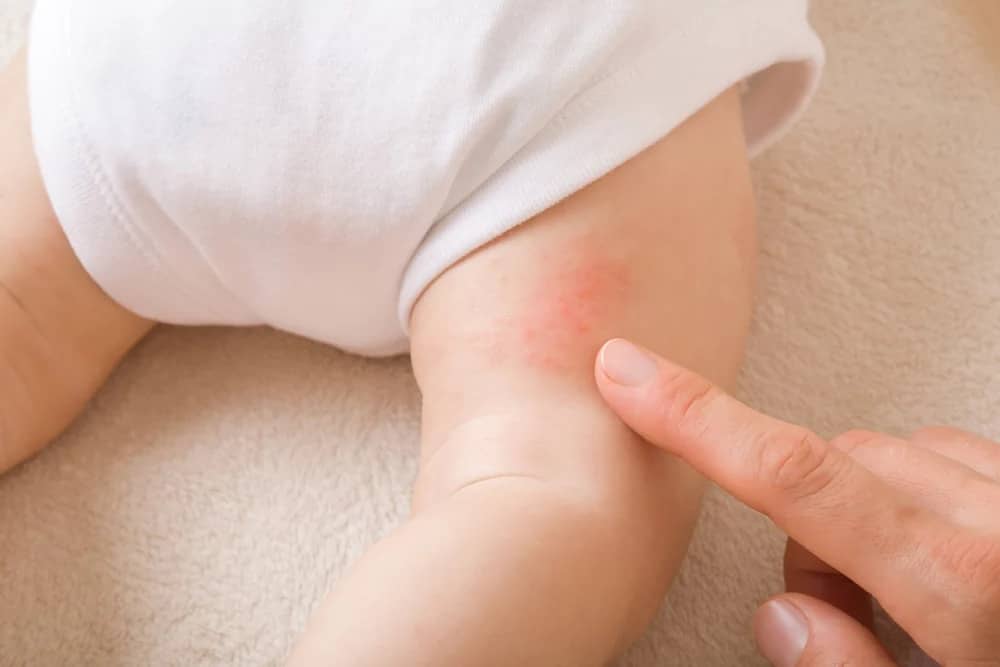
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease is a contagious viral infection caused by enteroviruses, most commonly the coxsackievirus A16. It primarily affects children under the age of five but can also occur in older children and adults. The disease gets its name from the characteristic sores and rashes that appear on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth.
HFMD is most common during the summer and early autumn months, but it can occur year-round in some regions.
Symptoms of HFMD
The symptoms of HFMD typically appear three to six days after exposure to the virus. This period is known as the incubation period. Common symptoms include:
- Fever: Often the first sign of HFMD.
- Sore Throat: Discomfort while swallowing.
- Mouth Sores: Painful red spots or ulcers on the tongue, gums, and inside of the cheeks.
- Skin Rash: Flat or raised red spots, sometimes accompanied by blisters, on the palms, soles, and sometimes on the buttocks and thighs.
- Fatigue: General sense of discomfort or feeling unwell.
Rarely, severe cases may lead to complications such as dehydration, viral meningitis, or encephalitis.
Causes of HFMD
HFMD is caused by enteroviruses, with coxsackievirus A16 being the most common culprit. The infection spreads through:
- Direct Contact: With nasal secretions, saliva, or fluid from blisters.
- Fecal-Oral Transmission: Poor hand hygiene after diaper changes.
- Respiratory Droplets: Coughing or sneezing.
The virus can survive on surfaces, making it easy to spread in schools, daycare centers, and other communal settings.
Diagnosis of HFMD
A doctor can usually diagnose HFMD based on the patient’s symptoms and the appearance of sores and rashes. Laboratory tests are rarely needed unless complications arise.
Treatment Options for HFMD
There is no specific antiviral treatment for HFMD. The focus is on relieving symptoms and preventing dehydration. Here are some ways to manage HFMD:
- Pain Relief:
- Use over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce fever and ease discomfort.
- Avoid aspirin in children due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome.
- Soothing Mouth Sores:
- Offer cold foods and drinks, such as ice cream or popsicles.
- Avoid acidic or spicy foods that may irritate sores.
- Hydration:
- Encourage fluid intake to prevent dehydration. Use oral rehydration solutions if necessary.
- Good Hygiene Practices:
- Regularly wash hands with soap and water.
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces and toys.
Most children recover fully within seven to ten days without medical intervention.
Preventing HFMD
While it’s difficult to prevent HFMD entirely, the following measures can reduce the risk of infection:
- Teach children to wash their hands thoroughly, especially after using the toilet or changing diapers.
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals.
- Keep children with HFMD at home until they are fever-free and their sores have healed.
- Regularly clean and disinfect shared items and surfaces.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Although HFMD is usually mild, consult a doctor if:
- Symptoms persist or worsen after 10 days.
- Your child shows signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth, reduced urination, or sunken eyes.
- Severe symptoms, like high fever or neurological issues, develop.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease, though unpleasant, is generally a mild and self-limiting illness. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help you manage it effectively and prevent its spread. By practicing good hygiene and monitoring your child’s condition, you can ensure a smooth recovery.











I haven¦t checked in here for some time because I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are great quality so I guess I¦ll add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂